Search This Supplers Products:Safety Light CurtainsMeasuring Light CurtainsLaser Scanning RadarSafety RelaysLaser Distance SensorSafety Mats
Sensor Output Types Explained: A Practical Guide for Industrial Automation
time2025/12/10

- Explore the main industrial sensor output types — from PNP/NPN discrete, analog (0–10 V / 4–20 mA), to RS-485, Ethernet, and safety-rated OSSD. Learn how to choose the right type for automation, measurement, or safety applications.
In industrial automation, understanding the types of sensor outputs is essential for designing reliable, efficient, and safe control systems. Although sensor applications vary—from position detection to safety interlocking—the underlying principle is the same: sensors detect a physical phenomenon and convert it into an electrical signal that your control system can interpret.
This guide provides a clear and practical explanation of the most common sensor output types used in modern automation environments, helping you determine which type is best suited for your application.
Discrete (Digital) Outputs: PNP / NPN / Relay / OSSD
Discrete outputs are binary signals that switch between two states: ON/OFF or HIGH/LOW. They are widely used in machine control, safety systems, and object detection.
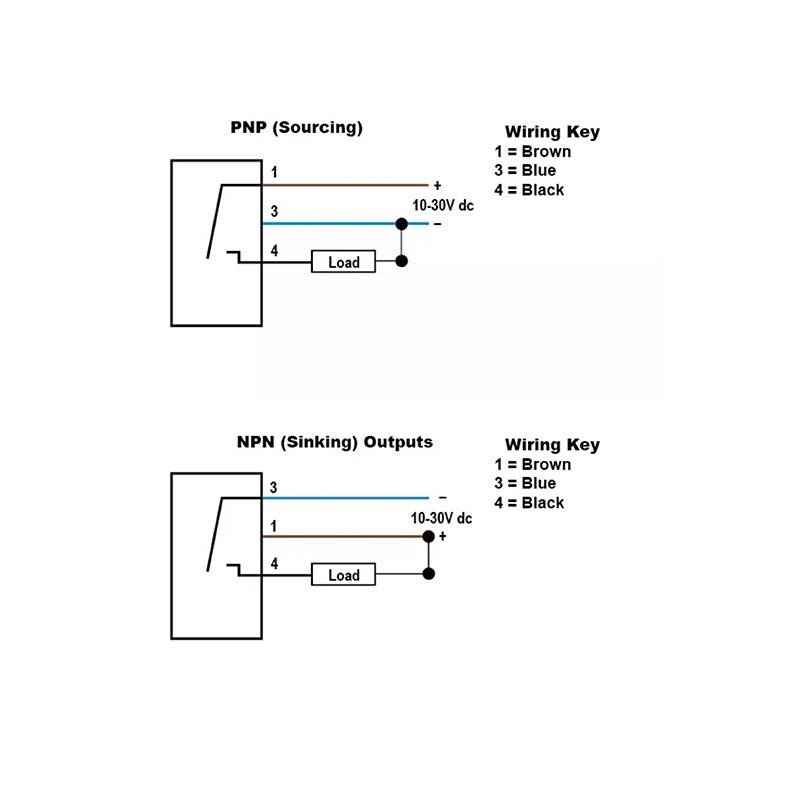
NPN and PNP Outputs
· NPN (Sinking Output)
The load is connected to the positive supply, and the NPN sensor pulls the signal line to ground when activated.
Best for systems using negative switching logic.
· PNP (Sourcing Output)
The load is connected to ground, and the PNP sensor drives the signal line to a positive voltage when activated.
Used widely across Europe and in most safety applications.
To learn more about the difference between NPN and PNP, see:
DADISICK Knowledge Base:
Relay Outputs
Relay outputs use an internal mechanical or solid-state switch.
They offer:
· High load capacity
· Electrical isolation
· No leakage current
Relay-output sensors are slower but extremely robust and suitable for high-power circuits.
Safety Outputs (OSSD)
OSSD is an output specifically designed for safety sensors such as safety light curtains and safety interlock switches, and it differs significantly from ordinary digital outputs. You can think of it as: OSSD = Super Output with Self-Test + Redundancy + Fault Monitoring.
OSSD Operating Characteristics Features include:
· Features dual-channel output; a fault on either side will trigger a safety shutdown.
· Continuously sends pulse signals for self-diagnosis.
· Indicates short circuits, open circuits, crosstalk, or internal faults in the controller.
· Meets ISO 13849-1 Performance Level (PL) requirements.
Analog Outputs: Voltage vs Current
Analog outputs provide a continuous electrical signal that is proportional to the measured physical quantity (distance, pressure, temperature, etc.).
Voltage Output (0–5 V / 0–10 V)
Advantages:
· Simple to use
· Good for short-distance signal transmission
Limitations:
· Noise-sensitive
· Voltage drop across long cables
Current Output (4–20 mA)
The most common format in industrial measurement and control systems.
Key benefits:
· Excellent noise immunity
· Long-distance transmission without significant loss
· 4 mA baseline provides line-break detection
This is widely used in laser displacement sensors and high-accuracy measurement devices.
Digital Communication Outputs: RS-485, IO-Link, Ethernet & More
With the development of smart factories, more and more devices are using digital communication to transmit data, rather than simply a set of electrical signals.
Common protocols:
RS-485 / Modbus-RTU
· Strong anti-interference capability
· Long-distance transmission capability
· Multi-device networking
· Low cost
Suitable for upgrading old factories, AGVs, and warehousing logistics.
IO-Link (Smart Sensor Technology)
IO-Link allows:
· Reading internal sensor parameters
· Uploading diagnostic information
· Communication with a single standard three-core cable
· Automatic device identification and configuration
Ideally suited for high-end automation.
Ethernet/Industrial Ethernet
Used for high-bandwidth, high-speed requirements, such as:
· Smart factory platforms
· Visual inspection
· Robot systems
It not only transmits measurement data, but also uploads health status, event logs, and fault diagnosis information.
How to Choose the Right Output Type: Key Considerations
When selecting a sensor, engineers should consider:
· Required signal type (digital, analog, or safety-rated)
· PLC or controller compatibility
· Cable length and electrical noise
· Need for diagnostics or multi-variable data
· Safety compliance requirements
For high-risk machinery, choosing safety-rated sensors with OSSD output is essential.
For precision measurement, analog output is more suitable.
For complex data collection, communication-based outputs offer significant advantages.
DADISICK offers a comprehensive range of safety-focused sensors and automation components specifically designed for industrial and machine protection applications.
Comparison Table: All Common Sensor Output Types at a Glance
| Output Type | Signal Style / Protocol | Advantages | Limitations / Conditions | Typical Industrial Applications |
| Discrete (Digital) | PNP, NPN, Relay, OSSD (safety) | Simple wiring, fast response, clear ON/OFF logic; OSSD supports safety functions with self-diagnostics | Only provides binary states; not suitable for measuring continuous values; relay is slower | Object detection, position sensing, limit switches, safety interlocks, safety light curtains |
| Analog | 0–10 V voltage output, 4–20 mA current loop | Delivers continuous measurement values; suitable for precise monitoring; current loop works well over long distances | Voltage signals degrade over distance/interference; requires correct input compatibility | Laser distance measurement, pressure/temperature/level sensors, process control |
| Digital Communication | RS-485, Modbus RTU, IO-Link, Ethernet / Industrial Ethernet | Multi-variable data, long-distance communication, high speed, device diagnostics, remote parameterization | Requires compatible controllers; more complex wiring and configuration | Smart sensors, PLC communication, condition monitoring, automation networks |
Safety Output (Dual-channel OSSD) | Safety-rated redundant outputs with real-time diagnostics | High reliability, fault-tolerant, auto-monitoring, supports SIL/PL safety compliance | Higher cost; requires connection to a safety controller or relay | Safety light curtains, safety scanners, door interlocks, robot guarding systems |
Conclusion: Matching Output Type to Application for Best Performance
Sensor output types determine how industrial machines understand and react to their environment. From basic PNP/NPN discrete signals to advanced Ethernet communication and OSSD safety outputs, each type has its own advantages and application scenarios.
By selecting the right output type and using reliable components, factories can achieve safer, smarter, and more efficient operations.
DADISICK will continue providing high-quality safety sensors and automation solutions to support global machinery manufacturers and industrial users.
Recommended Industrial Automation Safety Sensors
Beam spacing: 40mm<br>
Number of optical axes: 64<br>
Protection height: 2520mm<br>
Light barriers outputs (OSSD)2 PNP
Detection range: 2000 mm, 5000 mm
Material: Nickel-copper alloy
Connection type: 3pin/4pin with 2M cable
Maximum detection distance: 30-1500mm
Shell material: Plastic, ABS
Connection type: Cable, 4 cores, 2m
By converting from the laser into electrical signals. determine various characteristics,distance, displacement, or position.
Similar Posts You May Be Interested in